Introduction
Among all the 3D printing techniques, FDM Printing is by far the most popular. In fact, when most people think about 3D printing, they are thinking of FDM. To help you learn about FDM printing or how it can impact your business or career, we have created this thorough and detailed guide we have created on the most common aspects and questions related to this 3D printing technique.
What is FDM Printing?
The FDM in FDM Printing stands for Fused Deposition Modelling. It works by depositing layers of feedstock material through a heated nozzle on a print bed, adding layer by layer to create finished 3D products. It is also called Fused Filament Fabrication(FFF).
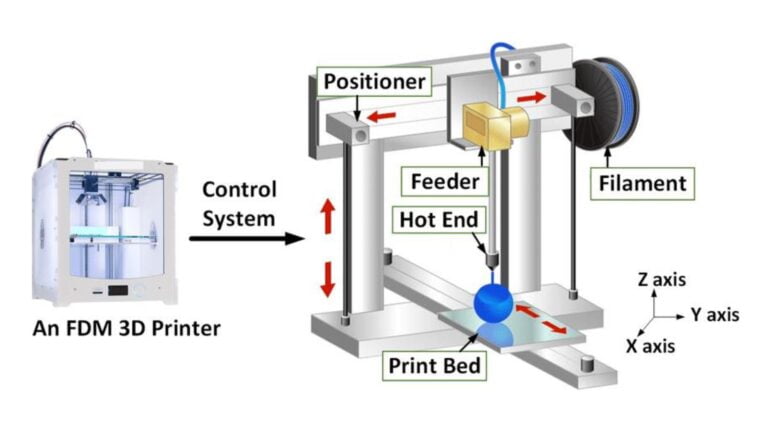

How does FDM 3D Printing work?
The general method for FDM 3D Printing is as follows:
- 3D design of the product is created on computer-aided design(CAD) software like SolidWorks or Fusion 360.
- This design is then adjusted into a slicer program like Cura to make it print-ready.
- The FDM 3D printer is calibrated, by leveling the bed and making sure all the parts are in working condition.
- This G-code file is fed to the printer.
- The printer starts pushing the printing material through its heated nozzle, depositing one layer on another over the print bed.
- Once finished, the product is taken off the print bed and sent for post-processing and quality assessment.
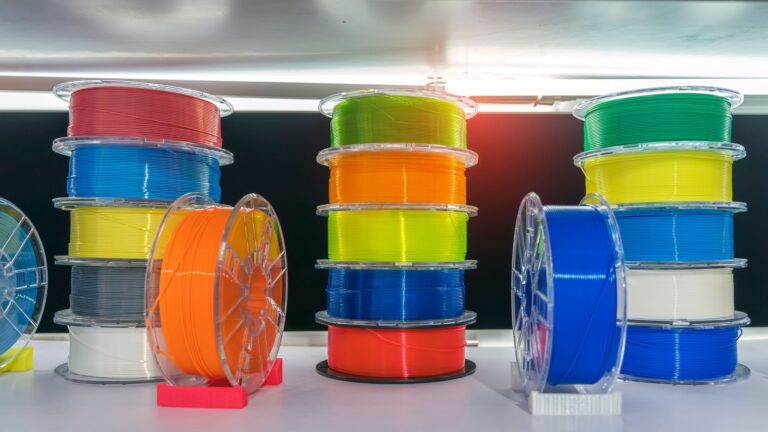


Materials in FDM Printing
FDM printing uses a wide range of materials, mostly thermoplastics, with varying material and engineering properties. These materials come in the form of wires or pellets made of printing material. Choosing which filament to use depends on budget, heat, chemical, or UV resistance, depending on the specifics of the project and where and how the products are designed for. Some of the most common materials used in FDM Printing are:
- PLA (Polylactic acid): the most popular option and widely available. It is factory compostable and very easy to print with.
- PetG (Polyethylene terephthalate glycol): Although similarly popular to PLA, PetG has superior heat and chemical resistance.
- ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene): It has a very high impact resistance. That makes it very suitable if you want to print something that can withstand higher levels of wear and tear.
- TPU (Thermoplastic polyurethane): Known for its elastic properties, TPU has a significant elongation limit and is resistant to tearing.Preferred for printing flexible products.
- ASA (Acrylonitrile styrene acrylate): Resistant to high levels of heat, it can take large amounts of thermal exposure. Ideal for industrial moving parts like gears.
Pros of FDM Printing
- Cost-efficient: Materials used in FDM printing are generally cheaper than materials used in other 3D printing technologies, like concrete or metal. On top of that, FDM printing machines have a very low entry to the barrier as they are priced attractively for not just big industries, but hobbyists as well
- Community support: As it is the most popular 3D printing technique, FDM printing has a big and knowledgeable community, both online and offline. Interacting in these communities, on Reddit or the Thingiverse forum, can help you overcome a lot of the early challenges and problems faced by beginners and experts.
- Faster printing: Compared to SLA and SLS printing, FDM offers the greatest speed. That is crucial if you’re using 3D printing as a solution for something like Rapid prototyping, where speed is a very significant factor. This only applies to the initial stages of product development, as resin printing is better in the later stages.
- Less post-processing: FDM requires little to no post-processing. The products created are ready to use. This also means there is less material wastage. That makes FDM an even more economical and sustainable option.
- Cheaper equipment: FDM printers and filaments are usually very attractively priced at the entry point. As there are so many players competing in this market right now, it is very easy to find great prices for amazing printers and quality printing materials as well. When looking at the wider context, SLA and SLA printers have way more expensive printers and materials, although that is fast changing.
- Safer process: The most common printing materials in FDM like PetG or PLA are non-toxic. You don’t need any special safety equipment like gloves or masks.
Cons of FDM Printing
- Inferior finish quality: if the surface finish is a high-level priority, FDM can be unsatisfactory. Since bonding between each surface layer is weaker, the grains of each line of material can be very visible. This leads to a low-resolution output, limiting FDM more suitable for printing functional parts.
- Needs lots of adjustments: Due to the many moving parts involved in the printing process, FDM printers require a lot of attention to ensure that the whole system remains aligned.
- More maintenance of printer: As it has more involvement of movement, the different parts of your printer can undergo a lot of wear and tear. This includes nozzle changes, cleaning the extruder, and calibrating the print bed before every print. This adds to upkeep hours as well as maintenance costs.
- Highly dependent on the quality of stock material: The quality of the end product depends a lot on the source material being fed into the printer. As many players have entered this lucrative and emerging market, there is always the chance that you get low-quality or derivate material. To avoid this, You should make your check out whoever is selling you the filament, especially if you are buying online.
- Size limitation: FDM Printers cannot print anything lesser than 0.3 mm in width. Although well-suited for larger printing jobs, this form of printing is not as precise as other techniques like resin when printing on a small scale.


How much does FDM 3D Printing cost?
The cost of printing with FDM depends on these factors:
- Material: Materials like PLA, PetG, ABS, etc are substantially cheaper to use. As they are the most popular options in the market, there is an abundance of supply, which keeps prices low. They are also suitable for most small and medium businesses, as well as the majority of hobbyists. Having said that, these options are not the best in terms of their engineering properties. On the higher end, you have higher-quality materials like PEEK, nylon, and carbon fiber which are preferred by enterprise-level manufacturers. They have better temperature resistance and impact strength than cheaper options like PetG or PLA.
- Size of print: This is pretty self-explanatory. A bigger print will always cost more, as more material is required. However, this rule also has an exception. Complex and detailed designs will take longer to print, as the printer speed has to be reduced to get more precision. Due to this, you may find that two prints that have the same weight and material may have differing costs.


FDM Printing Service from 3D Motifs
If you’re looking for an FDM Printing service from experts but don’t want to be charged with a bomb, you’re in the right place. At 3D Motifs, we have helped hundreds of our clients with quality design and 3D printing solutions at affordable prices. Contact our team today and let’s get printing.

